Rethinking School Suspensions: Unveiling Their Lasting Consequences and Pathways to Reform
How School Suspensions Shape Students’ Academic and Life Outcomes
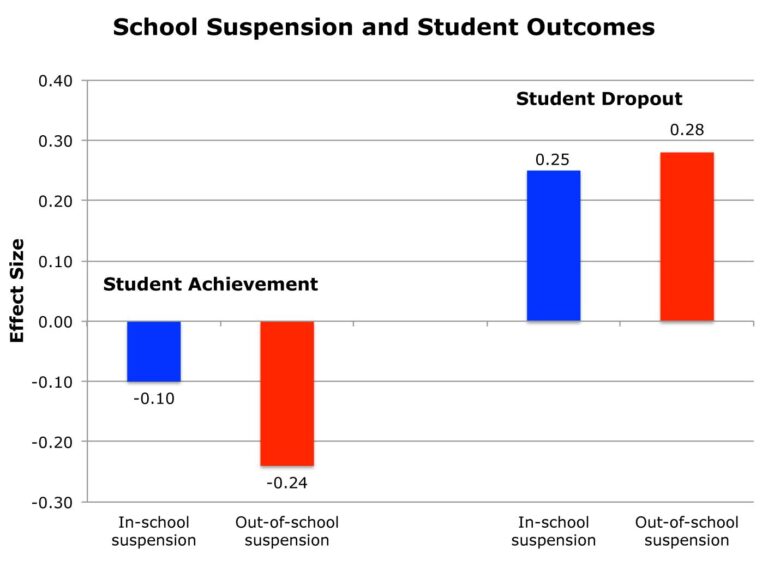
School suspensions have traditionally been used as a disciplinary measure to manage student behavior and uphold school order. Yet, mounting research reveals that these exclusions often inflict enduring harm on students’ educational progress and overall well-being. Interruptions caused by suspensions can disengage students from learning, leading to diminished academic performance, increased dropout rates, and fewer opportunities for higher education enrollment. This is especially true for students from disadvantaged backgrounds who frequently lack the resources or support to contest disciplinary decisions, thereby exacerbating educational disparities and limiting their future socioeconomic prospects.
Extensive studies have linked suspensions to several adverse long-term outcomes,including:
- Elevated chances of involvement with the juvenile justice system
- Greater risk of unemployment or underemployment in adulthood
- Increased mental health struggles stemming from social isolation
- Reinforcement of the school-to-prison pipeline,disproportionately affecting marginalized communities
| Area of Impact | Statistic | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Dropout Rate | Suspended students are 3 times more likely to drop out | National Education Association (2023) |
| Juvenile Arrests | Over 50% linked to school disciplinary actions | U.S. Department of Justice (2022) |
| College Enrollment | 20% decrease among suspended students | Institute of Education Sciences (2023) |
Challenges Students Face When Contesting Disciplinary Actions
Many students encounter formidable obstacles when trying to appeal or challenge suspensions.These difficulties often arise from a lack of knowledge about their rights, limited access to legal or advocacy resources, and insufficient institutional support. As a notable example, students from low-income or non-English-speaking households may struggle to understand complex disciplinary policies or navigate appeal procedures. Moreover, schools frequently fail to provide transparent information or accessible channels for students to advocate for themselves, leaving many unaware of their options.
- Confusing and opaque disciplinary guidelines
- Absence of legal portrayal or advocacy within schools
- Fear of retaliation or harsher penalties
- Distrust toward school officials and disciplinary systems
- Insufficient staff training on supporting student rights
| Barrier | Effect on Students | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Information Deficits | Students unaware of appeal rights | Implement clear dialog and outreach programs |
| Resource Scarcity | Lack of access to legal counsel or advocates | Establish school-based legal aid partnerships |
| Fear of Reprisal | Hesitation to report or contest suspensions | Create anonymous reporting and support systems |
| Systemic Bias | Unequal disciplinary treatment | Conduct bias awareness training and regular policy reviews |
Confronting Disparities in School Discipline: A Call for Equity
Disciplinary practices in schools disproportionately impact students of color, often intensifying existing systemic inequalities rather than addressing the underlying causes of behavioral challenges. Research indicates that Black and Latino students are suspended at rates two to three times higher than their white counterparts for similar infractions. This disparity not only disrupts their education but also increases their risk of dropping out and entering the juvenile justice system. To counteract these inequities, schools must shift away from rigid zero-tolerance policies and adopt restorative approaches that emphasize healing and accountability.
- Provide implicit bias training for educators and administrators
- Design culturally responsive behavioral interventions
- Expand access to mental health and counseling services
- Involve families and community stakeholders in reform initiatives
Ongoing openness through data collection is vital for tracking progress and ensuring accountability. The table below highlights suspension rates by demographic group, underscoring the urgency for reform:
| Demographic Group | Suspension Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Black Students | 15% |
| Latino Students | 9% |
| White Students | 5% |
| Asian Students | 2% |
Strategic Policy Initiatives to Protect Vulnerable Students
To better support students vulnerable to suspension, educational institutions must prioritize restorative justice over punitive discipline. Implementing conflict resolution programs empowers students to voice concerns and collaboratively resolve disputes. Comprehensive training for educators on cultural competence and trauma-informed care is essential to prevent disproportionate disciplinary actions against marginalized groups. Additionally, expanding mental health services can address behavioral issues proactively, reducing the need for suspensions.
Policy reforms should also guarantee transparent, fair disciplinary procedures, including simplified appeal processes accessible to all students, especially those lacking advocacy. Allocating funds for intervention specialists and mentorship programs can strengthen support networks within schools. The following table summarizes key policy components designed to safeguard at-risk students:
| Policy Component | Objective | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Restorative Justice Circles | Facilitate collaborative conflict resolution | Decrease in repeat suspensions |
| Guaranteed Appeal Rights | Ensure equitable disciplinary reviews | Enhanced due process protections |
| Trauma-Informed Educator Training | Improve responses to student triggers | Stronger student-teacher relationships |
| Expanded Mental Health Services | Address root causes of behavioral issues | Reduction in suspension rates |
Conclusion: Toward Fair and Supportive School Discipline
The repercussions of school suspensions extend well beyond temporary exclusion, often disrupting the futures of students who lack the means to contest these decisions. As reported by NBC News,the absence of accessible appeal mechanisms leaves many vulnerable students isolated in facing disciplinary consequences. Meaningful reform requires systemic changes that prioritize fairness, transparency, and support—transforming suspensions from a default punishment into a last-resort measure. By embracing equitable policies and restorative practices, schools can uphold discipline while protecting the rights and potential of every student.