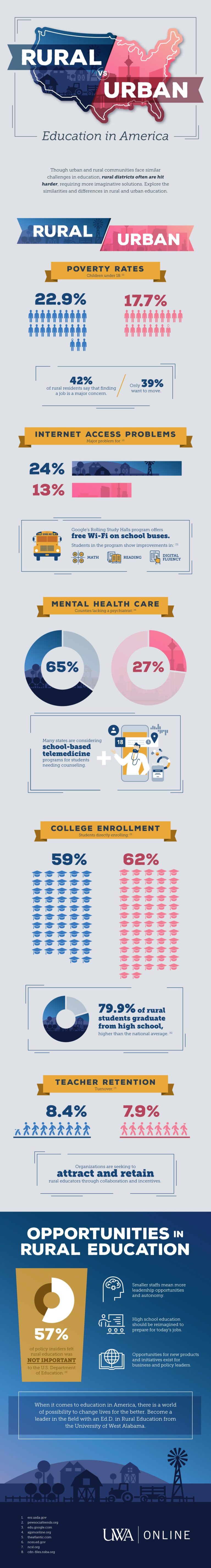
Addressing the Distinct Challenges Facing Rural Schools in America
Recent research has illuminated the distinctive difficulties rural schools in the United States encounter, setting them apart from their urban and suburban peers. As concerns about educational inequality grow nationwide,this in-depth study highlights the multifaceted barriers rural educators,students,and communities must overcome. These include chronic underfunding, teacher shortages, limited technological infrastructure, and aging facilities. The report emphasizes the critical need for customized strategies to bridge these gaps and promote fair educational opportunities for rural learners.
Infrastructure Challenges Unique to Rural Education
Rural educational institutions frequently grapple with obstacles rooted in their geographic remoteness and constrained local resources. Many schools operate in aging buildings lacking modern amenities, which hampers efforts to deliver quality education on par with urban districts. Basic utilities and internet connectivity are frequently enough unreliable, complicating the integration of digital tools and limiting extracurricular offerings.
Primary infrastructure hurdles include:
- Restricted budgets due to smaller tax revenues,limiting facility upgrades and expansions
- Challenges in recruiting and keeping skilled staff in isolated areas
- Long transportation routes that increase commute times and reduce student participation in after-school activities
- Insufficient broadband access,curtailing remote learning and digital engagement
| Challenge | Consequences | Approximate Percentage of Rural Schools Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Deteriorating Facilities | Unsafe environments leading to lower attendance rates | 65% |
| Limited Broadband | Hinders e-learning and digital skill progress | 47% |
| Teacher Shortages | Fewer course offerings and increased staff turnover | 54% |
| Transportation Difficulties | Restricts access to extracurricular programs | 39% |
Overcoming Teacher Recruitment and Retention Barriers in Rural Settings
Attracting and maintaining qualified educators remains a persistent challenge for rural schools,directly influencing student achievement. Factors such as limited housing availability, geographic seclusion, and fewer opportunities for professional growth deter many teachers from committing long-term. Additionally, educators often manage multi-grade classrooms with scarce resources, intensifying feelings of isolation and burnout.
Key contributors to recruitment and retention difficulties include:
- Non-competitive salaries relative to urban districts
- Limited local support systems for teachers and their families
- Restricted access to up-to-date technology and teaching materials
- Transportation challenges affecting daily commutes and participation in school events
| Retention Issue | Effect on Rural Schools | Suggested Interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Isolation | Elevated turnover rates | Relocation incentives, virtual mentorship programs |
| Resource Limitations | Decline in instructional quality | Enhanced funding, collaborative resource-sharing |
| Professional Development Gaps | Skill deficiencies and low morale | Online training sessions, peer support networks |
Bridging the Resource and Technology Divide in Rural Schools
Access to essential educational resources and technology remains uneven in rural districts, adversely affecting teaching and learning quality. Many schools report outdated devices and unreliable internet connections, which are vital for both classroom instruction and remote learning. This digital gap limits student engagement and restricts teachers’ ability to employ innovative teaching strategies. Recent statistics reveal that only 61% of rural schools have adequate broadband speeds, compared to 92% in suburban areas, placing rural students at a important disadvantage.
Funding shortages further compound these issues, restricting the purchase of modern hardware and software. The report identifies critical needs such as:
- Up-to-date computing equipment: Many rural classrooms still rely on obsolete laptops and tablets, impeding digital literacy.
- Targeted professional training: Educators need specialized instruction to effectively incorporate technology into their teaching.
- Technical support availability: Limited IT personnel result in slower troubleshooting and increased classroom disruptions.
| Resource | Access Rate (%) | Impact on Education |
|---|---|---|
| High-speed Internet | 61 | Delays in content delivery and fewer interactive learning tools |
| Modern Devices | 54 | Reduced participation in digital assignments |
| Technical Support | 40 | Increased downtime and interruptions during lessons |
Strategic Policy Initiatives to Promote Equity in Rural Education
Closing the educational gap in rural communities demands focused, long-term policy measures that reflect their unique circumstances.Allocating increased funding specifically for rural districts can help address resource shortages, enabling investments in technology, infrastructure, and specialized personnel. Additionally, incentive programs such as housing assistance, student loan forgiveness, and career advancement opportunities are vital to attract and retain skilled teachers, mitigating chronic staffing deficits.
Expanding broadband access is another critical priority, as reliable internet connectivity underpins modern digital learning. Collaborative efforts among state governments, local authorities, and community organizations can foster innovative, context-sensitive solutions‚ÄĒranging from mobile technology labs to virtual mentorship networks.The following summarizes essential policy recommendations for stakeholders committed to fostering equitable educational outcomes:
- Dedicated Funding: Grants earmarked for rural infrastructure improvements and educational materials.
- Teacher Incentives: Competitive pay, professional development pathways, and community integration support.
- Broadband Expansion: Investments to ensure high-speed internet access for all rural schools and households.
- Community Collaboration: Partnerships with local organizations to enhance student engagement and support services.
| Policy Focus | Main Goal | Anticipated Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Boost financial resources for rural districts | Upgraded facilities and enriched educational resources |
| Teacher Support | Enhance recruitment and retention | Lower turnover and improved teaching quality |
| Connectivity | Expand access to high-speed internet | Improved digital learning experiences |
| Community Engagement | Strengthen partnerships with local entities | Greater student support and enrichment opportunities |
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Rural Education Advancement
As rural schools continue to face a complex array of challenges‚ÄĒfrom funding limitations and staffing shortages to technological inequities‚ÄĒthis report highlights the pressing need for targeted interventions and sustained investment. Addressing these issues is crucial not only for the success of rural students and educators but also for advancing educational equity across the nation. Policymakers, educators, and community leaders must collaborate to implement innovative, tailored solutions that empower rural schools and ensure all students have access to high-quality education.